4 Major Casting Process Flows, Surface Treatments and Applications

Posted on : June 17th, 2025,By GREFEE
GREFEE-Precision Casting
Writer: Christopher Role: Manufacturing manager
In the field of industrial manufacturing, precision casting technology is a key link in shaping high-quality components. As a leader in the industry, GREFEE has manufactured a large number of compliant parts for various regions worldwide by virtue of its in-depth research and innovative application of processes such as investment casting, lost foam casting, shell molding, sand casting, and a sound quality management system

Investment Casting in Casting Processes
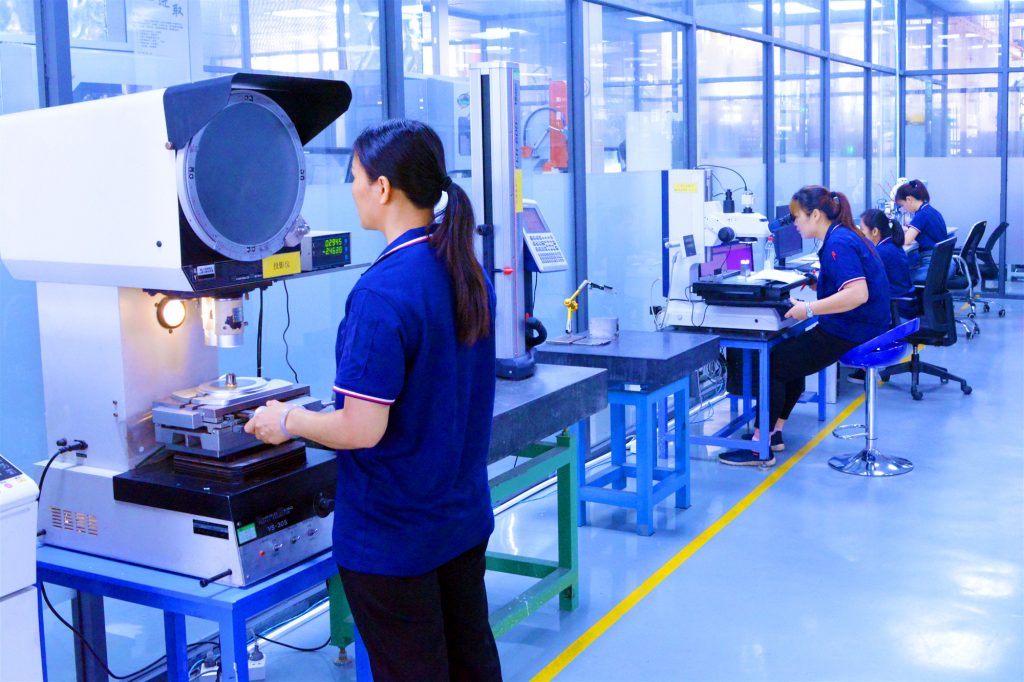
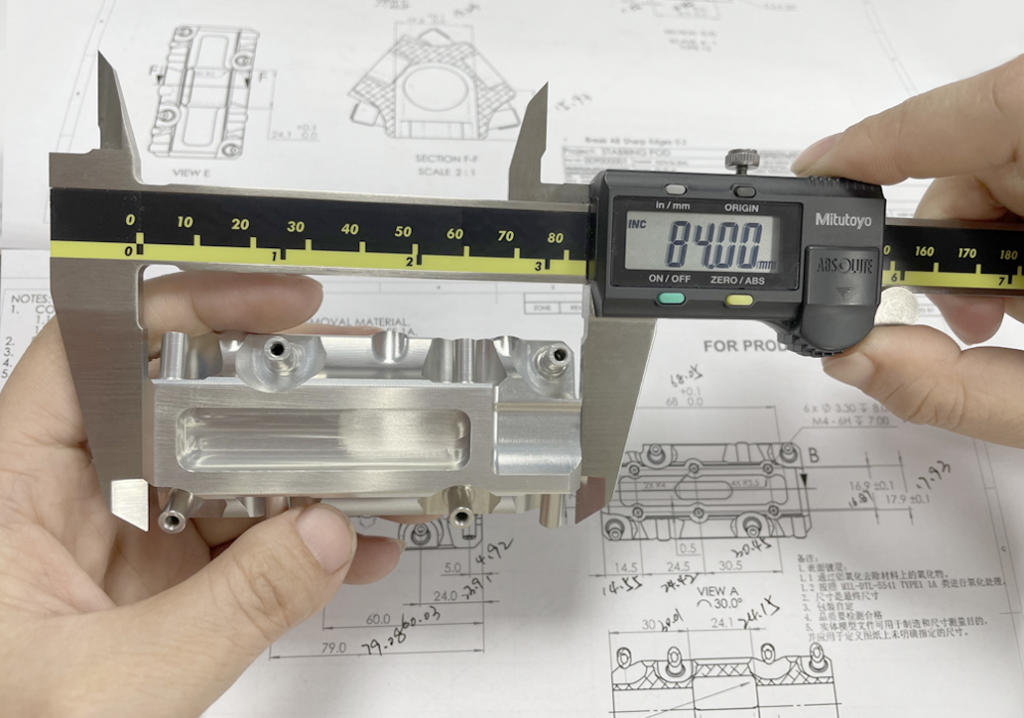
Investment casting is one of GREFEE’s most distinctive precision casting processes. Each part cast by GREFEE’s investment casting process undergoes 20 rigorous procedures before being delivered to customers. This includes 5 inspections to ensure quality: raw material testing before slurry injection, hardness testing after production, surface roughness inspection, internal flaw detection, and final three-dimensional (3D) measurement. These five tests safeguard each part to ensure it meets design requirements.
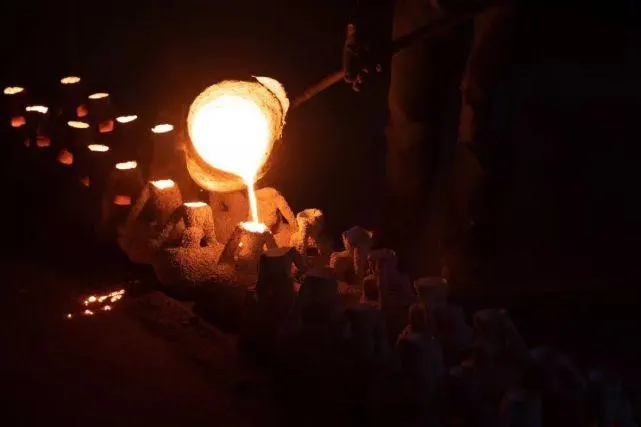

In terms of surface treatment, GREFEE adopts processes such as sandblasting, polishing, and electroplating according to the characteristics of investment casting parts. Sandblasting can remove impurities and oxide scales from the surface of castings, giving them a uniform rough texture; polishing further improves surface finish to meet the appearance requirements of high-precision products; electroplating not only enhances the corrosion resistance of castings but also imparts different decorative effects according to customer needs.
With the extremely high precision of investment casting and its capability to shape complex structures, GREFEE’s products play an important role in fields such as precision components for medical devices and exquisite housings for lighting equipment. For example, in medical devices, investment-cast surgical instrument components have minimal dimensional errors, meeting the strict precision requirements of surgical operations; in lighting equipment, the produced housings feature exquisite shapes and high surface finish, combining practicality and aesthetics
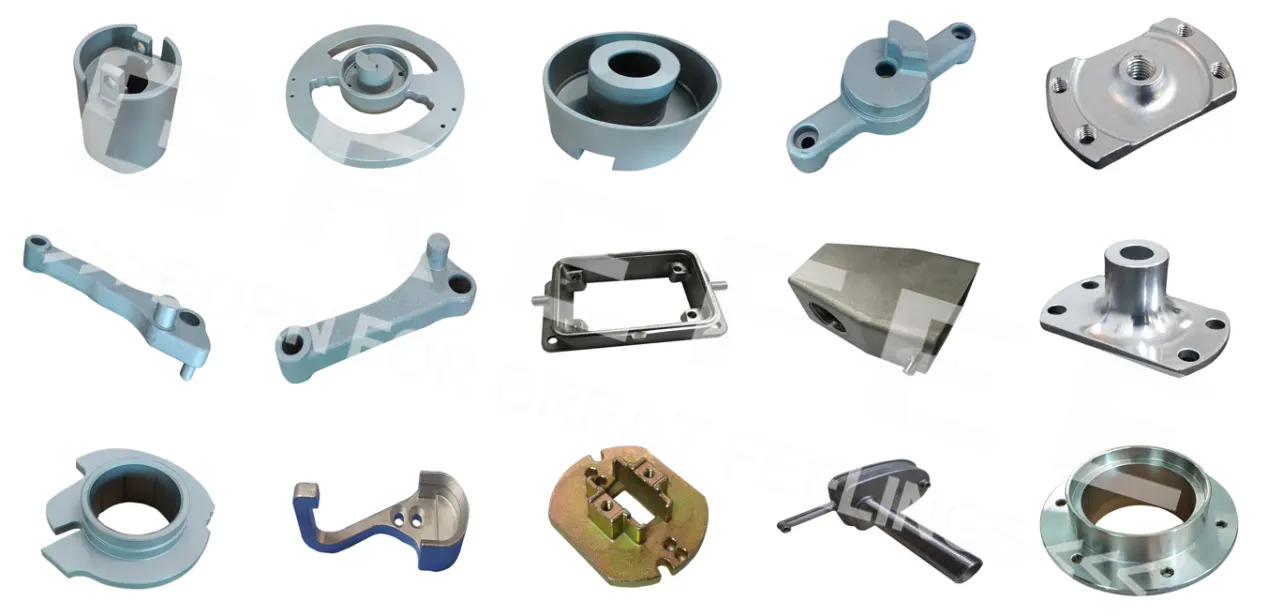

Precision Casting: Lost Foam Casting
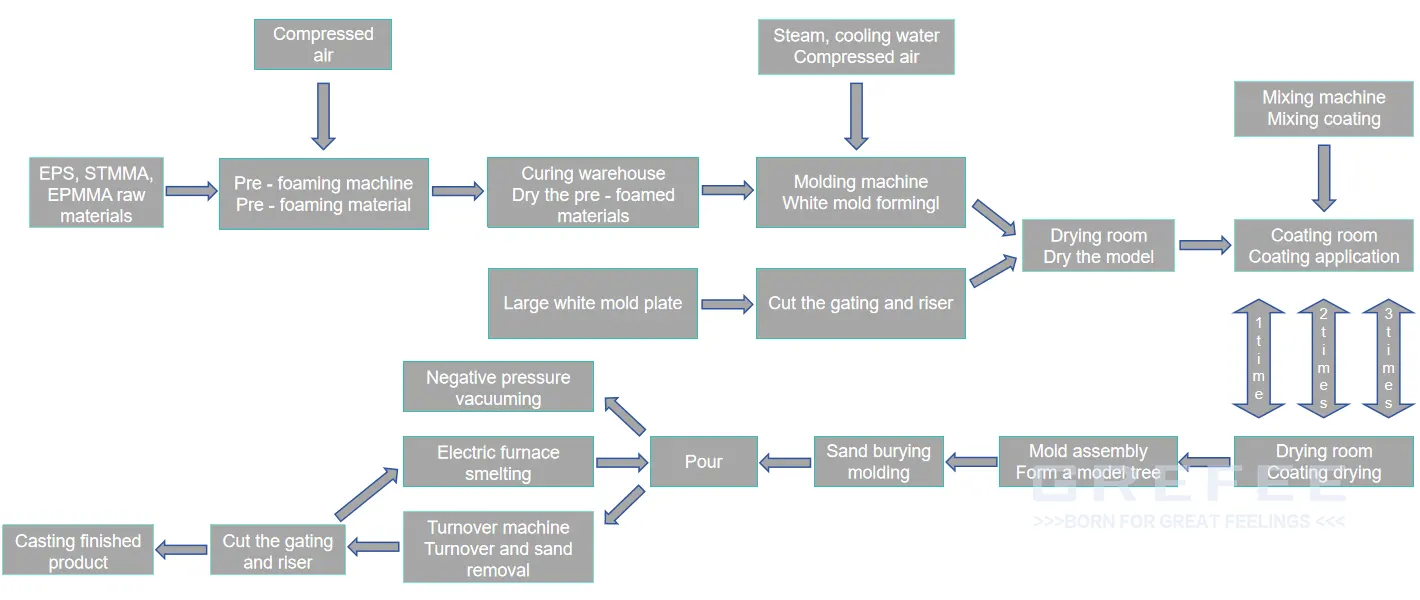
The lost foam casting process stands out in GREFEE’s production system. As an innovative casting technique, its remarkable feature lies in using foam plastic patterns (such as EPS, STMMA, or EPMMA) as the mold, combined with binder-free dry sand and vacuum technology for casting. This technology is widely applicable to casting various materials
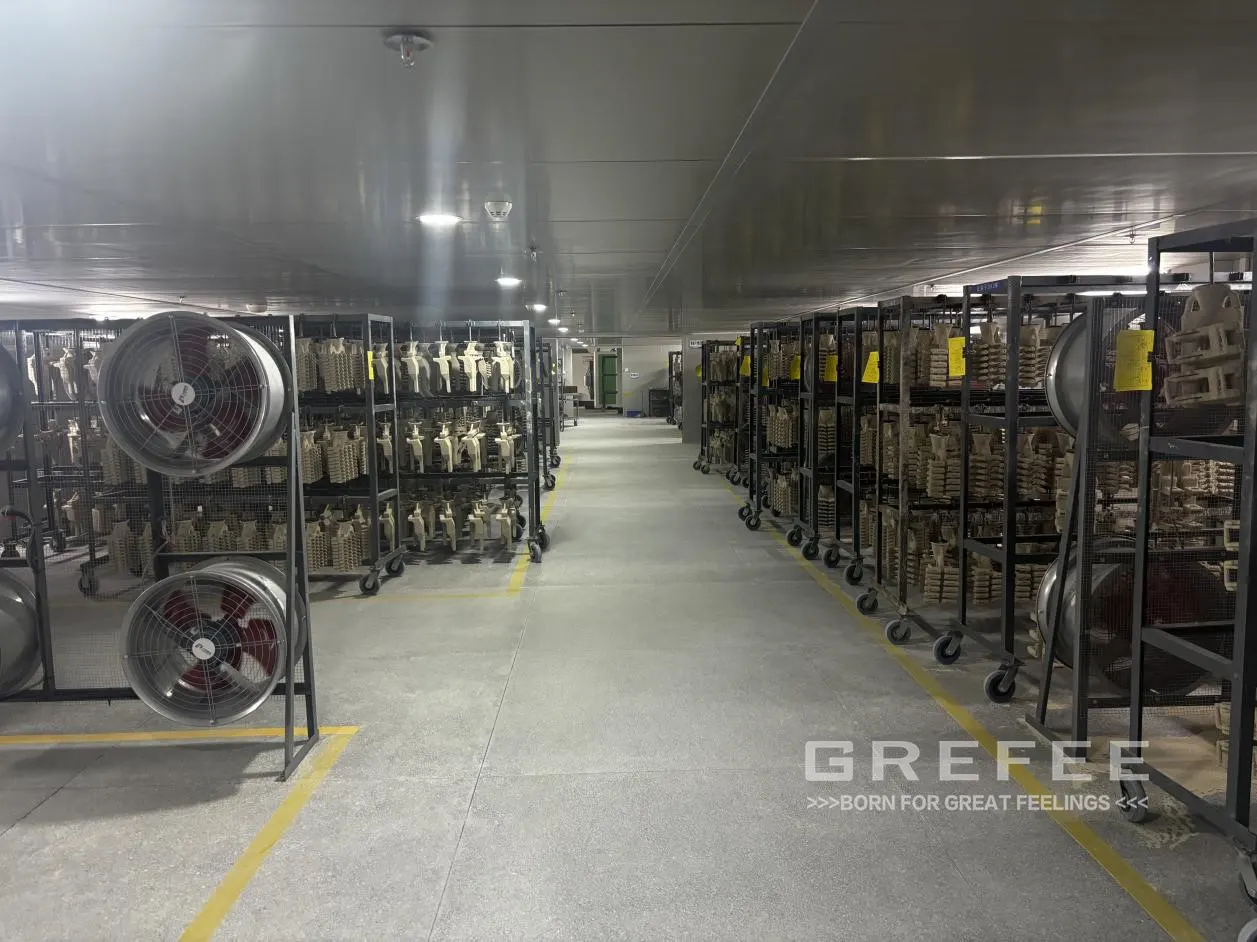

Process Flow: First, a foam plastic model identical to the shape of the casting is fabricated. The foam plastic model not only exhibits excellent moldability but also completely vaporizes and disappears during the casting process. Next, the model is placed in a specially designed sand box, which is filled with dry sand and compacted to form a solid mold. Subsequently, high-temperature molten metal is poured into the mold. The heat from the molten metal rapidly vaporizes and eliminates the foam plastic model, with the vacated space filled by the molten metal. Upon cooling, the casting is obtained
Advantages of Lost Foam Casting Process
High Casting Precision: Lost foam casting can produce castings with precise shapes and high surface finish. As the foam pattern is similar in size and shape to the casting, and the pattern vaporizes during pouring, the liquid metal directly occupies the pattern’s position, ensuring dimensional accuracy and shape consistency of the casting. This reduces costs for subsequent cleaning and machining. It is particularly suitable for producing castings with high dimensional accuracy and complex shapes, ensuring that castings are formed in one go according to dimensional precision requirements.
High casting quality and low production cost: The internal structure of castings is dense, with significantly reduced internal defects. It enables large-scale mass production of castings and significantly reduces costs.
Wide range of cast materials: This technology is suitable for casting various materials, including non-ferrous metals, gray iron, and general steel castings, demonstrating high material adaptability.
High production efficiency: Lost foam casting enables large-scale mass production, while reducing machining allowances and labor consumption, thus improving production efficiency.
Low rejection rate: The technology simplifies mold design and sand treatment systems, reducing internal defects such as air holes and slag inclusions, thereby lowering the rejection rate.
Environmental protection and energy saving: During lost foam casting, the gas generated by the vaporization of the foam model is relatively minimal, and used sand can be recycled, aligning with emission reduction and energy-saving goals.
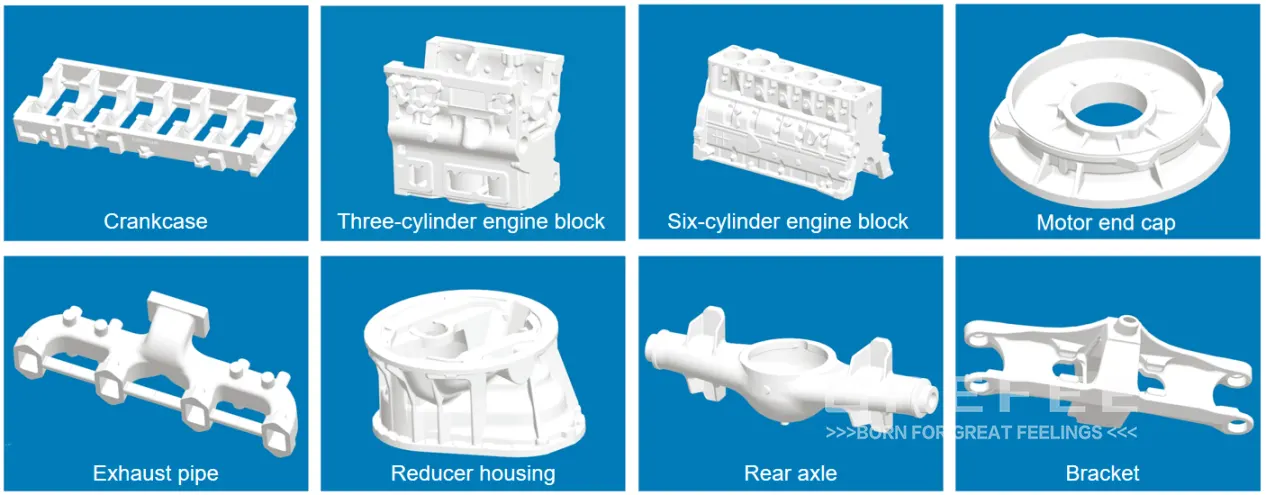
At the same time, since lost foam casting does not require mold drawing, it can achieve integrated forming of complex structure castings with high production efficiency, which has obvious advantages in the manufacturing of large parts such as engine blocks in the automotive industry and box bodies of truck accessories. Taking the automotive engine block as an example, its complex internal structure and precise dimensional requirements can be perfectly realized through the lost foam casting process, which can effectively guarantee the performance and reliability of the engine.
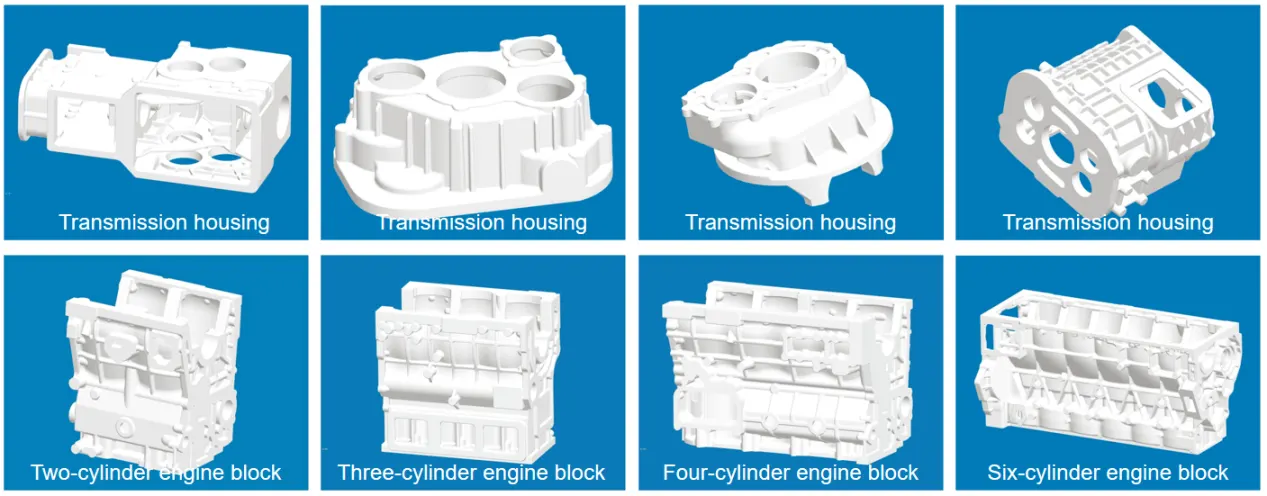
Precision Casting: Shell Molding
Shell molding is one of the many precision casting processes, mainly used for producing castings with complex shapes and high dimensional accuracy. It is widely applied in automotive, aerospace, machinery, and other industries

Shell molding is a casting method that uses resin sand as the molding material. It forms a thin-shelled mold by heating the template to melt and harden the resin sand, and then performs pouring. The core of this process is to utilize the curing characteristics of resin sand under heating conditions to create a thin-shell mold with certain strength and permeability. During production, the resin-coated sand is first heated to a specific temperature, causing it to melt and solidify on the mold surface, forming a thin and strong shell.
After the shell is completed, multiple shells are combined into a mold, followed by pouring of molten metal. Once the casting cools and solidifies, the outer shell is broken to remove the casting
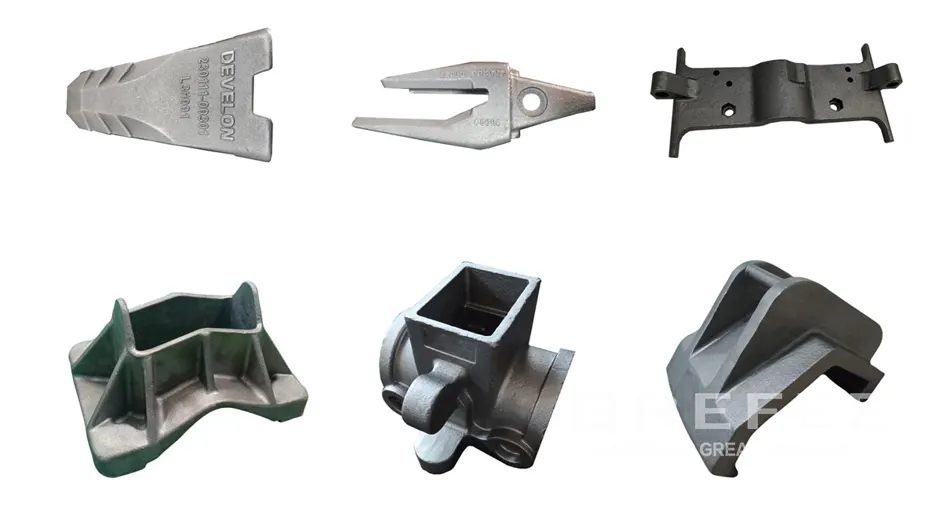

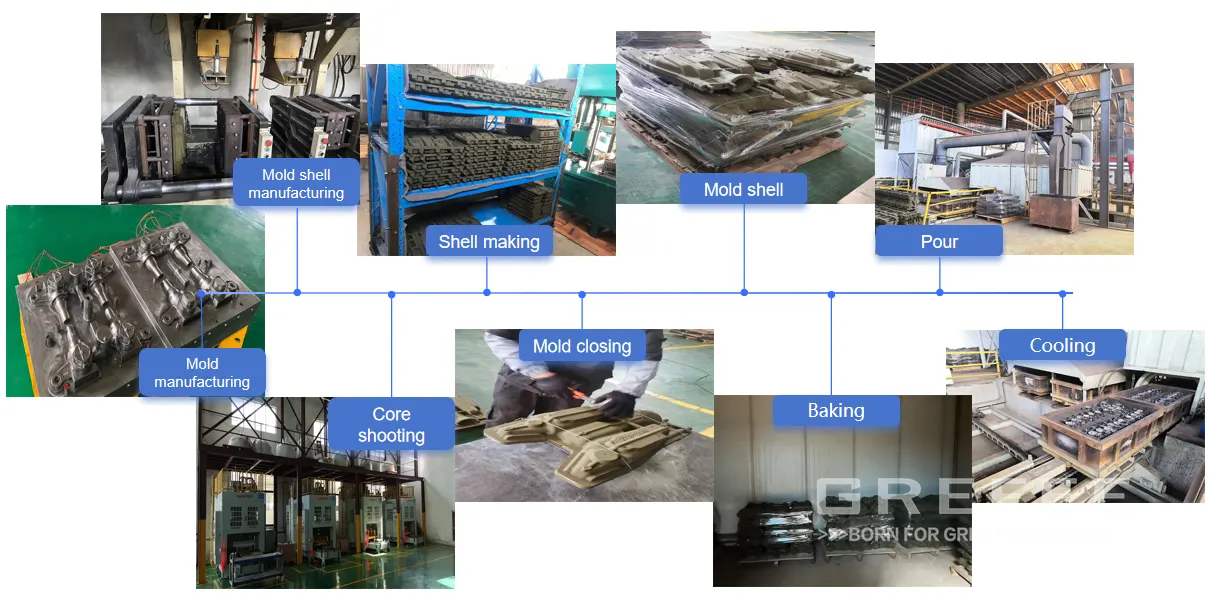
Shell Molding Process Flow
Mold Manufacturing: Fabricate metal molds. For each casting, produce two half-molds, including a pouring cup.
Shell Mold Manufacturing: Set parameters such as mold heating temperature, pressure, and time. After heating the mold, inject mixed coated sand granules into the mold cavity through an automatic sand shooter. Once the sand mold solidifies, a thin shell forms inside the mold, which is then removed.
Mold Closing: Clamp and fix the two shell molds with fixtures, and evenly apply coating to seal the gaps between the shells to form a complete shell mold.
Baking: Place the closed shell mold in an oven for baking to remove moisture, improve air permeability, and enhance the shell’s strength.
Sand Filling: Place the baked shell mold into a sand box, inject sand into the shell to secure it, and compact the sand by vibration.
Casting: Pour liquid material into the shell mold, allowing it to flow through the pouring gate into each cavity of the mold tree.
Cutting: After the cast shell and casting fully solidify and cool, use vibration equipment to separate the shell from the casting. Perform preliminary sand cleaning and shot blasting to remove adhering sand from the casting blank. Then cut the castings from the mold tree.
Shaping and Finishing: Grind the pouring gates flat using grinding wheels or machining, including rough grinding, fine grinding, and precision trimming. Finishing repairs surface defects (e.g., sand holes, slag inclusions, burrs, bulges, deformation) through grinding, welding, shaping, and shot blasting. After passing visual inspection, the castings are transferred to the heat treatment line for different processes.

Precision Casting: Sand Casting
As a traditional and widely applied process, sand casting still holds an important position in GREFEE’s production. Its production process includes steps such as molding, core making, mold closing, and pouring. First, a mold is used to shape the molding sand, forming a cavity corresponding to the shape of the casting. Then, a sand core is made to form the internal structure of the casting. After placing the sand core into the cavity, the mold closing operation is carried out. Finally, molten metal is poured into the cavity, and after cooling and solidification, the casting is removed
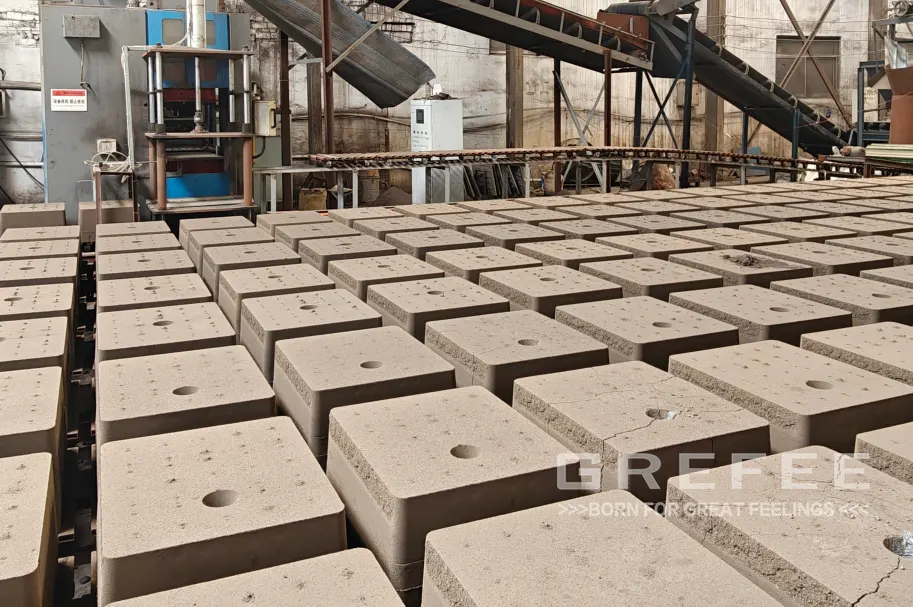

For surface treatment of sand casting products, methods such as cleaning, shaping, and surface coating are commonly used. Cleaning removes molding sand and burrs from the casting surface, shaping corrects dimensional deviations of the casting, and surface coating imparts good appearance and protective properties to the casting. It is widely applied in the production of large structural parts for truck accessories, conventional components for mechanical parts, etc. For example, large structural parts like truck frames can be efficiently produced by sand casting to meet market requirements for product quantity and cost.
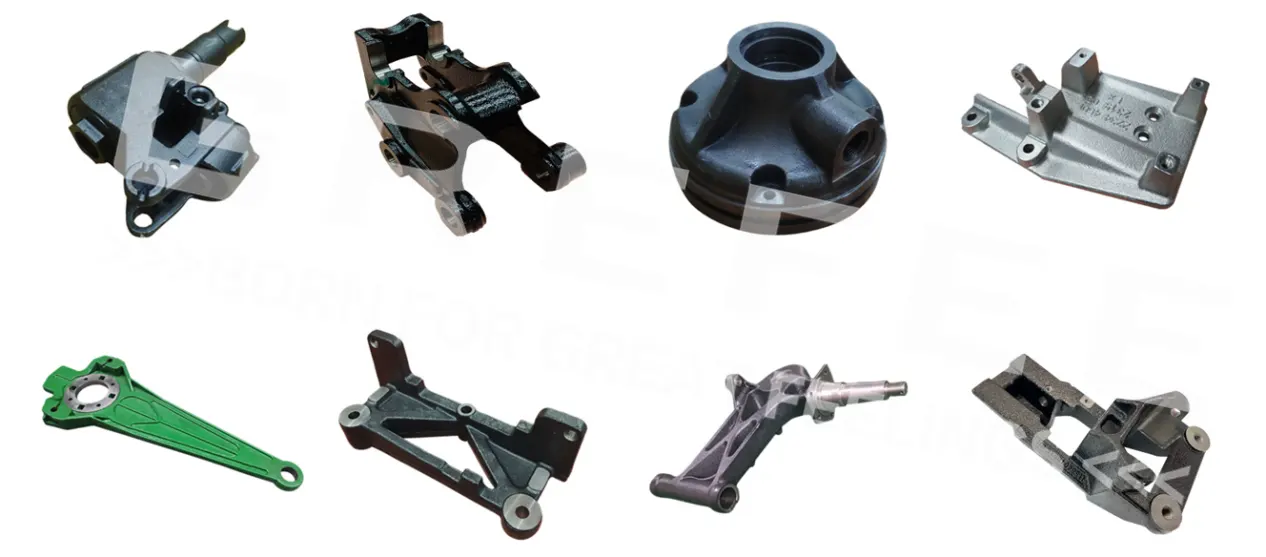

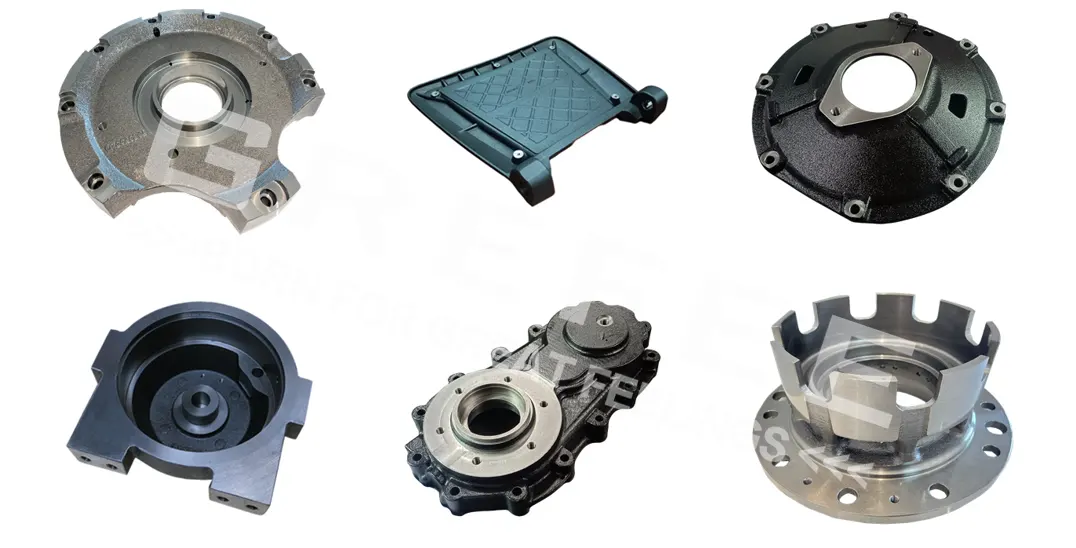
Relying on its exquisite mastery of precision casting processes such as investment casting, lost foam casting, shell molding, and sand casting, as well as perfect production processes and surface treatment technologies, GREFEE continues to deliver high-quality products in the fields of automotive industry, mechanical parts, truck parts, medical devices, lighting equipment, household equipment, etc. In the future, GREFEE will continue to deepen its precision casting technology, continue to innovate and break through, and provide reliable product support and technical guarantee for the development of more fields.

MORE BOLG
Insert mold in injection mold service
What are advantages and disadvantages of Zinc alloy and Aluminum alloy?
Inspection standards for injection molded partappearance
How to judge the quality of your plastic products?
Inspection standards for CNC machining
To ensure that your products are 100% qualified
Categories

Try GREFEE now,for free
We keep your uploaded files confidential and secure.