What are the common types of threaded holes?
How to process threaded holes with CNC machining?

Posted on : June 18 , 2022 By GREFEE
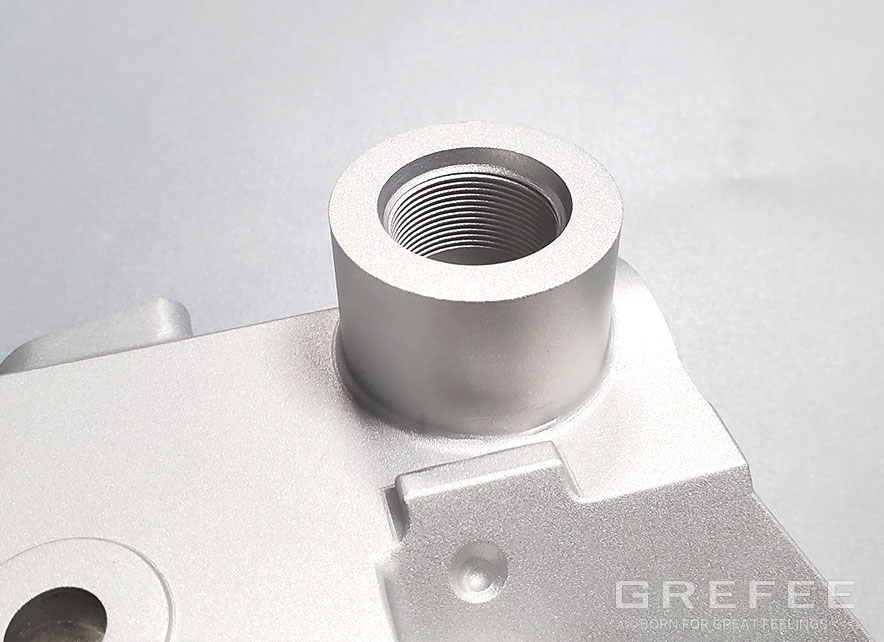

Threaded holes fabrication: cutting and forming
There are many types of screw thread in processing the threaded holes. The internal thread can be processed with the cutting tools (cutting tap or single lip cutting tool) or with a forming tap. Even though two methods bring the same effect. However, the following factors should be taken into account before selecting any method:
- Part material hardness
- Size of threaded hole
- Blind hole or through hole
- Use appropriate machines
- CNC parts quality
For threaded holes below M6, we can process with the traditional cutting or forming tap. For threaded holes above M6, single lip cutting tool is commonly used.
Processing the threaded holes on the hard material, we can use a cutting tap because its groove provides enough space for the metal slags to overflow and a pathway for the cooling agent or lubricate to flow down to the cutting edge.
When processing the soft and colored metals (aluminum, brass, copper, or lead) or the drilling holes, no chips are generated but the long strip material. We can use the forming tap. Pay attention to the force related to the material movement as the forming tap will distort the inlet holes (outlet hole of through-hole) and lead to deformation.
Maintain standards
Maintaining the current standards will eliminate the need for specific tools, reduce the machining cycle and save costs. A ready-to-use scheme is an optimal choice, which means to stick on the screw thread sizes in your areas/countries and be familiar with the types of screw thread. What’s more, it is better to provide tools in the workshops. However, customized solutions are the optimal choice but always set up the design as the priority.
Correct position of threaded holes
Ensure that the whole diameter of the threaded hole is included in the part. Keep in mind that the outer diameter will be larger than the internal screw thread diameter. If the threaded holes are too close to the margin of parts, the screw threads might penetrate through the side surface of parts and cause damage to the surface finish, tap, cutting tools, or the integrity of the parts.
If there is a need for extra thickness to contain the threaded holes, adds an emboss on the various parts of screw thread.
Manage angled surface
It might be harder to process the threaded holes into the oblique surface.
If adds the threaded holes onto the current bevel, it needs a groove to create a plane first. So, the threaded holes might be added from this plane. Drilling and tapping on the angled surface might break the transitional tap —— ordinary tools are not designed for the uneven bending force due to tapping.
If an angled surface does not exist, add the threaded holes on the parts first and then process the angled curve surface. After this, make sure that the depth of the threaded holes is in alignment with the design requirements.
Types of threaded hole
There are two types of threaded holes, which are blind holes and through holes. Each segment should be considered thoroughly in the designing stage to ensure they can be processed without interfering with other characteristics.
Blind threaded holes
Threaded holes cannot penetrate the parts. If the holes are processed with the end mill, the bottom is probably a plane. If the holes are processed with the traditional drilling heads, the bottom might be a cone. If the full thread needs to extend to the bottom of the blind threaded hole, deal with the bottom tap immediately.
The blind threaded hole marks must specify the depth of the drilling holes and threads on 2D drawing
Through threaded hole:
Through threaded hole has inlets and outlets on both sides of parts or features. Part thickness must be considered as the length of the tap or cutting tools might not be sufficient to squeeze the whole deep hole. If the the tap or cutting tools is not long enough to drill a hole from one side, consider one of the following factors:
Add threads within the allowable depth of the tap or cutting tools. Be aware of that a section of the hole may not have screw thread.
Add threads on both sides of holes with an allowable depth of tap and cutting tools. Be aware of that the crew thread do not align at intersections.
Add threads on both sides of holes with an allowable depth of tap and cutting tools. Be aware of that the screw thread may not touch each other and a promotion of the hole will be unthreaded.
Deep threaded hole
A deep threaded hole refers to the depth of threads that is more than 1.5 times screw thread diameter. Deep threaded hole processing is challenging. There is more heat generated when the tools contact the parts. As it needs a higher cutting force, the risks of damage will increase.
Be aware of the processing parameters and the geometrical shape of the tap or tool. Consider decreasing the cutting and feeding speed to reduce the force on the tap or cutting tools. Select a faucet with a large groove to remove the debris faster and allow more cooling agents or lubricate to reach the cutting edge.
Screw thread processing method:
1.Tap processing method
(1). Classification and characteristics of tap machining
Process the threaded holes with tap is a common method, which mainly suits for threaded holes with small diameter (D<30) and low position accuracy requirement.
In the 1980s, the flexible tapping method is used quite often to process the threaded holes. It uses the flexible tapping collet to clamp the tap and then the tap collet can be utilized for axial compensation to compensate for the feed errors due to the non-synchronization between the axial feed of the lathes and spindle velocity for a correct pitch.
Thus, rigid tapping has been the primary method for thread processing.
It uses the rigid spring collet to hold the tap and the lathe to ensure consistency between the feeding and rotating speed of the spindle. Compared to the flexible tapping collet, the spring collet is cheaper with a wider application range and is simply structured. Besides the clamping tap, it can also clamp the end mills and other cutters, reducing the cost of tools. Meanwhile, the rigid tapping allows high-speed cutting, increases the efficiency of the machining center, and lowers the fabrication cost.
(2). Ascertain the thread bottom hole before tapping
The processing of the threaded bottom holes has a huge influence on the service life of the tap and the processing quality of screw thread. Generally, the diameter of the threaded bottom holes should be close to the upper limit of the diameter tolerance of the threaded bottom hole. For instance, the diameter of the bottom of the M8 threaded holes is Ф6.7+0.27mm, and the bit diameter is Ф6.9mm. This can extend the service life of the tap by minimizing the processing allowance and the load of the tap.
(3) Tap selection
The first thing to do when selecting taps is to consider the processing material accordingly. Tool companies produce different types of a tap according to the materials. It should be noted that the tap is very sensitive to the processing material compared with the milling cutter and boring cutter. For instance, processing the aluminum parts with the tap used for casted iron will lead to thread dropping, disorderly screwing, and even tap breaking. Apart from that, the difference between the through-hole tap and blind hole tap should be paid attention to, too. The front end of the through-hole tap is long, and the chip removal is at the front. The from-end of the blind hole is short, and the chip removal is from the rear. Process the blind holes with the though hole tap cannot ensure the processing depth of the screw thread. Moreover, we should pay attention to the diameter of the tap handle and the width of the square when adopting the flexible tap collet. They should be the same as the tap collet. The diameter of the tap shank for rigid tapping shall be the same as that of the spring jacket. Overall, correct tap selection guarantees efficient processing.2.
2.Thread milling method
(1). Characteristics of thread milling
Thread milling adopts the thread milling tool, machining center three-axis linkage, which is the x-axis and y-axis arc interpolation, and z-axis linear feed milling method to process threads.
Thread milling is mainly used to process large hole threads and thread holes of difficult-to-machine materials.
(2). Major characteristics
Fast processing speed with high efficiency and processing accuracy. The material of tools is hardening alloy material but feeding speed is fast. The screw thread accuracy is high due to the high fabrication accuracy of tools.
Milling cutters are widely used as it reduces the tool cost significantly. No matter it is the left hand thread or right hand thread, as long as it is the same pitch, one tool is enough for various parts of screw thread processing.
Milling processing is convenient for chip removal and cooling, which is better for tap, especially for the aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and thread processing of materials that are hard to process. It is well-particular suited for the large-scale components and the thread machining of parts and components made of precious materials.
Sine there is no front-end of tools, it suits for processing the blind hole with short threaded bottom hole and holes without retracting groove.
(3). Classification of thread milling tools
Thread milling tools can be divided into two types, one is the machine clamp carbide cutter, and the other is the integral carbide cutter. The clamping tool has a wider application range since it can process holes with a screw thread depth less than the length of the blade but can also be machined with a thread depth greater than the length of the blade. Integral carbide milling cutter suits holes with screw thread depth less than the tool length.
3.Snap method
(1). Characteristics of snap method
It is possible to encounter large threaded holes on the box parts. A method similar to lathe pick-up can be used to install the thread turning tool on the boring bar to bore the thread without taps and thread milling cutter.
(2). Dos and Don’ts for snap method
After the main shaft is started, there shall be a delay time to ensure that the main shaft reaches the rated speed.
During the retracting, if the thread tool is manually ground so the tool cannot be grinned symmetrically and cannot reverse to retract. The main shaft orientation must be adopted, then the tool moves radially before retracting.
The fabrication of the cutter bar must be accurate, especially the portion of the cutter groove must be consistent. In case of the inconsistency, multi-tool bar processing is not allowed. Otherwise, it will lead to disorderly deduction.
Even if it is a thin buckle, it cannot be picked at one time, or it will cause the tooth loss and poor surface roughness. It should be finished by two cuts at least.
Low processing efficiency, suits for single or low volume production, as well as special thread pitch and no according tools.
Understanding these principles and rules will be beneficial to the parts of threaded holes. GREFEE provides good design and robust fabrication capacity to turn your idea into reality. Let us see how we can meet your needs by contacting our customer service.
MORE BOLG
Insert mold in injection mold service
What are advantages and disadvantages of Zinc alloy and Aluminum alloy?
Inspection standards for injection molded partappearance
How to judge the quality of your plastic products?
Inspection standards for CNC machining
To ensure that your products are 100% qualified
Categories

Try GREFEE now,for free
We keep your uploaded files confidential and secure.