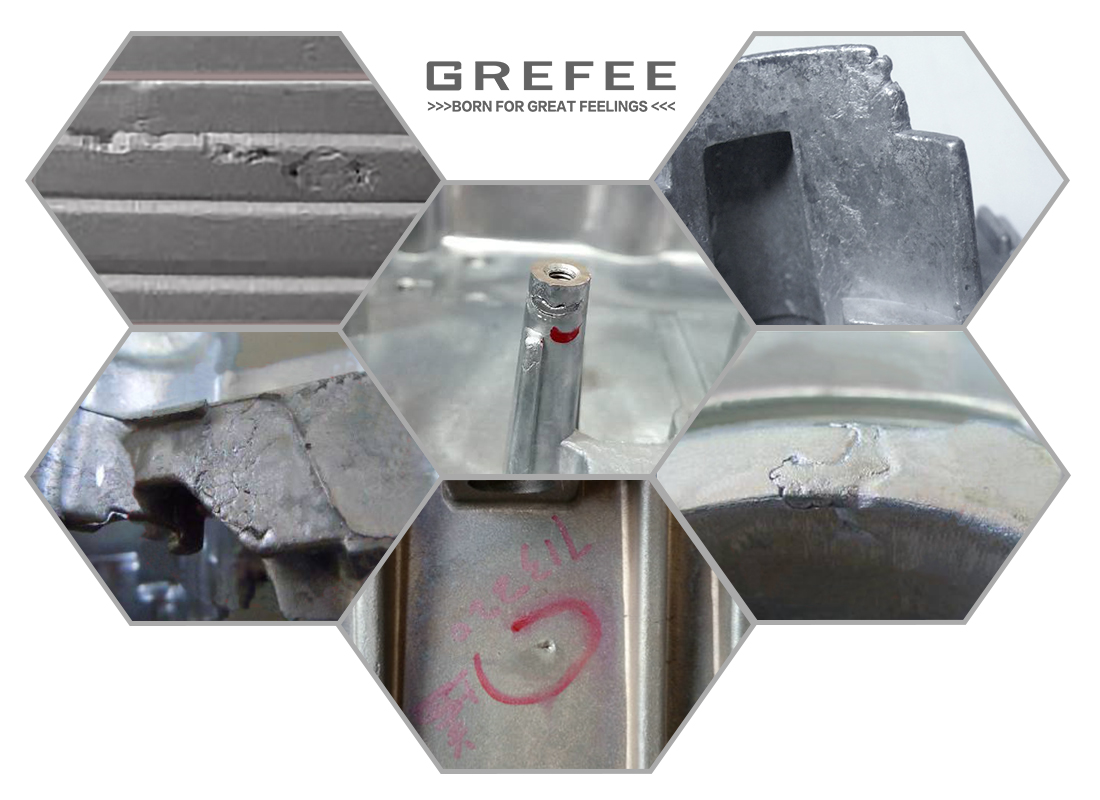
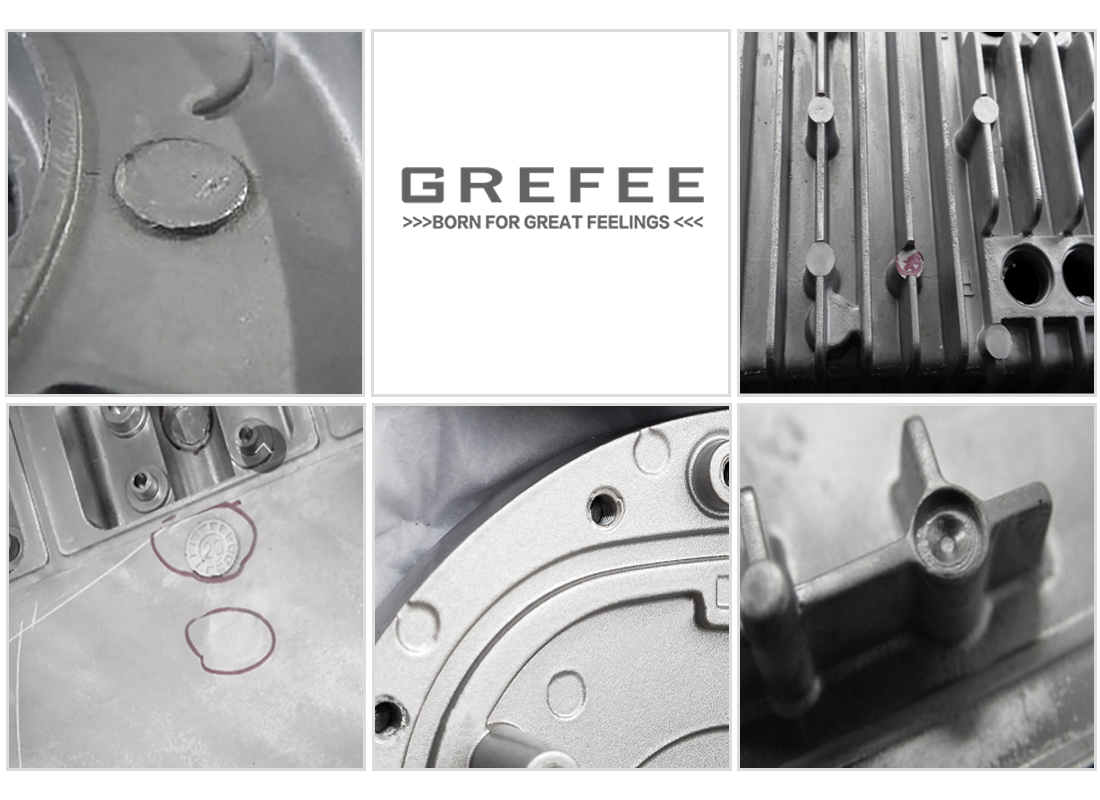
Problems you might meet in die casting

Posted on : June 8, 2022 By GREFEE

The die casting technology is widely used in many industries, such as automotive making, electronic engine shells, hardware, mechanics, aerospace, LED, etc. it is also a rigorous production process, which is inevitable to meet various troubles. With many years of experience, GREFEE has accumulated rich experience in die casting. This is an introduction to the common problems in die casting with solutions. You can also contact our engineers for support.
1. What is the specific pressure of injection? How to adjust it?
Answer: the injection-specific pressure is the liquid metal pressure in the chamber on a unit area. Try to use low specific pressure to ensure the quality. The specific pressure of the lamp decoration is normally lower than 50 MPA. The high the wall thickness, the higher the specific pressure is. The requirement of the specific pressure increases as the complexity of the products’ structure.
2. What is injection speed? How to adjust the injection speed?
Answer: the injection speed refers to the moving speed of the injection head during die casting. It is divided into slow injection speed and quick injection speed. The injection speed usually means the high injection speed. An appropriate low injection speed value is when the injection head passes through the pouring slot with no metal liquid flashes, which is 0.1~0.5M/S, and the value for quick injection speed for aluminum alloy is 0.1~1.1M/S. The thinner the aluminum alloy castings’ wall thickness, the higher the injection speed is. The more complex the aluminum castings’ shapes, the higher the injection speed is. A larger projected area needs a higher injection speed. The longer the filling routes, the higher the injection speed is.
3. What is pouring temperature? How to select the pouring temperature?
Answer: the pouring temperature refers to the average temperature when the metal liquid fills the injection chambers and mold cavities. The temperature should be as low as possible to ensure the molding and surface quality requirements. The pouring temperature of the aluminum alloys is 650℃~720℃. The alloys with good fluidity should be treated at low temperatures. For the thin-walled aluminum casting with complex shapes, we should increase the temperature. As Large die casting molds dissipate heat quickly, we can select a high pouring temperature.
4. What is die casting mold temperature? What is the mold temperature of the aluminum alloy die casting mold during the normal production?
Answer: the mold temperature is the temperature of die casting molds during production. The standard temperature of the aluminum alloy die-casting molds in production is 200℃~280℃. The thinner the wall thickness, the more complex the structure is, and the higher the temperature is.
5. What is filling time? How to select the correct filling time?
Answer: The time required for the liquid metal to enter the cavity until it is filled is called the filling time. The filling time of aluminum alloy die casting is 0.01S~0.1S. The selection principle of filling time is: (1) if the alloy pouring temperature is high, the filling time is longer. (2) if the die casting mold temperature is high, the filling time is longer (3) if the thick place is far away from the inlet, the filling time is longer (4) if the alloys have high melting heat, the filling time is longer (5) if the venting effect is poor, the filling time is longer.
Answer: holding pressure time is how much time needed when the liquid metal filling out the cavity and is solidified under the increased specific pressure. Its function is to make the solidified metals crystallize under pressure to obtain aluminum alloy castings with a dense internal structure. The pressure holding time for die casting aluminum is 1-2 sec when the wall thickness is less than 2.5MM and 3~8 sec when the wall thickness is 2.5~6MM. The selection principle is: (1) crystalized temperature range of the die casting alloys is large, so the pressure holding time is longer (2) the wall thickness of casting is big, so the pressure holding time is longer (3) the pressure holding time of the top gate, the pressure holding time is longer. The thicker the inlet, the longer the pressure holding time is.
7. What is retention time? How to decide the retention time?
Answer: the retention time is also called the cold molding time, which is the castings stay in the molds, from the beginning of the pressure holding to the casting ejection after opening the mold. Enough retention time ensures the mold can be solidified and cooled in the cavity with a certain level of strength. Usually, the period that no deformation and cracks are suitable. The retention time for the aluminum alloys castings is 5s ~ 30s. It is related to the wall thickness directly. The thicker the wall thickness, the longer the retention time is.
Die casting coating
1. What is die casting coating?
Answer: the die casting coating is used for spray painting the mold cavity walls, mold core surface, the friction parts of the die casting molds, and die casting machines ( such as the slide, ejector element, punch head, and the injection chamber). The die casting coating is generally the mixture of the lubricating materials and the dilute agent.
2. What is the function of the die casting coating?
Answer: (1) good lubrication performance under high temperature
(3) Reducing the heat conductivity of molds and keeping the fluidity of the melting alloys to improve the formability of the alloys.
(4)Reducing the friction between the casting and the forming parts of the mold to reduce the abrasion of the core and cavity to extend the service life and improve the surface quality.
3. What is the requirement of the die casting coating?
(1)Low volatilization point,dilute at 100~150 degrees can volatilize quickly.
(2) Good coating performance
(3) No corrosive action to the molds and castings
(4)Ggood lubricity
(5)Stable performance
(6)No special odor, and do not precipitate or decompose harmful gases under high temperatures.
(7) Simple preparation process
(8) Rich source and low price
4. What are the common aluminum alloy die casting coating?
Answer: (1) graphite + oil, largely used for forming parts, shooting punch, injection chambers
(2) Petroleum + asphalt, proportioning 85:15, heating the asphalt to 80 degrees, and adding petroleum to mix them evenly after melting, which prevents it from sticking to the mold.
(3)Colloidal graphite, used for chamber and injection punch (available in market).
(4) water based coating to dilute the spray agent to prevent the cavity surface from sticking to the mold.
The characteristics of defects, causes, and preventions of the castings
1. Features of the flow marks and the textures of castings
Answer: (1) characteristics: on the casting surface, some stripes are in the same direction as the flow marks. Obviously, the subsequent metal is different from the base without the textures and does not tend to develop.
(2) Causes:
- The liquid metal entries into the cavity will create a thin but incomplete metal layer. A bonding mark made up due to subsequent liquid metal
- Low mold temperature
- Small inlet section area and improper position will create splashes.
- Insufficient pressure on the liquid metal
- Too much coating
(3) Preventions:
- Increase the mold temperature
- Adjusts the section area of inlet and positions
- Adjusts the speed and pressure of the liquid metal in the inlet
- Appropriately selecting the coating and adjusting the use amount
2. Causes and preventions of the net burrs and crazing of the castings
Answer: (1) characteristics: on the castings’ surface, there are hair form extrusion marks, and they are expanding and elongating as the time of the die casting increases.
(2) Causes:
- Crazing on the mold cavity surface
- Incorrect mold material or improper heat treatment processing
- The mold temperature difference is too much
- The pouring temperature is too high.
- The preheat of the die casting molds is insufficient
- Rough cavity surfaces
- The strength of the mold insert is low or with sharp corners
(3) Preventions:
- Selecting the correct mold material and heat treatment processing
- The pouring temperature should not be too high, especially for the alloys with high melting points.
- The die casting mold should be preheated sufficiently.
- The die casting molds should receive regular annealing treatment or after several times of production. Grinding the surface of the forming part.
3. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of cold-shut
Answer: (1) characteristics: on the castings’ surface, there are irregularly, evident, sinked linear patterns (penetrable and in-penetrable), which are long and narrow. Some of these patterns has smooth bonding edges, some are likely to break off.
(2) Causes:
- Two strands of liquid metal are connected. Due to incomplete melting and no impurities in between, the bonding force of the two strands of metal is weak.
- Pouring temperature or mold temperature is low
- Inappropriate selection of alloys, poor fluidity
- Incorrect gate position or the flow path is too long
- Low filling speed
- Specific pressure of injection is low
(3) Preventions:
- Increases the pouring temperature
- Increases the specific pressure of injection, shortens the filling time
- Increases the injection speed and section area of the inlet
- Improves the venting conditions
- Correctly selects alloys, increases the fluidity of the alloys.
4. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the defects (sinks)
Answers: (1) characteristics: there are smooth depression (like a disk)on the surface of the thick parts.
- Contraction: A. Inappropriate design of the castings’ structure, the difference of wall thickness is too much. B. High contraction of alloys. C. Improper inlet position. D. Low specific pressure of injection E. Temperature of the partial mold is high.
- Air trapping: When filling the cavity, the local gas is not discharged. The air is compressed between the cavity surface and the liquid metal level
(3) Preventions:
- Wall thickness should be uniform
- Excessive thickness should be eased
- Select alloys with low contraction ability
- Selects the correct alloy liquid lead-in position and increases the section area
- Increases the injection pressure and increases the filling time
- Lowers the pouring temperature and mold temperature appropriately
- Cooling the partial high temperature places
- Improves the discharge conditions
5. Characteristics, causes and the preventions of the impressions
Answer: (1) characteristics:
- The contact mark of the casting’s surface and and cavity surface
- There is ladder trace on the castings’ surface.
(2) Causes:
- Caused by the ejection elements:①The end face of the ejector rod is worn;②The ejector rod is not adjusted properly;③the spliced part of the mold cavity and other parts do not match properly
- results from the splicing:① results from the inlaying;②movable part loose or worn;③the side wall surface is made of the inserts inserted between moving and fixed molds.
(3) Preventions:
- Inspects before working, repairs the die casting molds.
- The ejector rod should be adjust to the proper position.
- Fixes the insert and other moving parts.
- Eliminates the mosaic forms and improves the molds’ structure.
6. Characteristics, causes, preventions of the cold shots
Answer: (1) characteristics: there are cold shots on the surface and the metal particles that haven’t melt with the castings (usually at the undercasting positions)
(2) Causes:
- Inappropriate pouring system setting
- High filling speed
- Liquid metal flow into the cavity earlier
(3) Preventions:
- Improves the gate system to prevent the liquid metal from impacting the core, and wall.
- Increases the inlet section area
- Improves the operation and adjusts the machines.
7. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the the adhesion traces
Answer: (1) characteristic: A small piece of metal or nonmetal object is welded with the base part of the metal. The small pieces fall off under the external force. Some of the casting’s surfaces are brightening, and some are gloomy.
(2) Causes:
- There are metals or non-metal residuals on the surface of the mold cavity.
- Impurities sticking on the cavity surface when pouring.
(3) Preventions:
- Cleans the cavity, chamber, pouring system, and adhesive substances on the cavity surface before die casting.
- Cleans the pouring liquid metals.
- Selects the appropriate coating. Spraying evenly.
8. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the lamination (lamination and peeling)
Answer: (1) characteristics: evident metal lamination on partial casting
(2) Causes:
- The toughness of the die casting mold is not enough. When the liquid metal is filling, the mold plate vibrates.
- Poor coordination between the injection punch and the chamber. unstable speed when the injection punch is moving forward.
- Inappropriate design of the gate system
(3) Preventions:
- Increases the toughness of the mold, fixes the mold parts to make it stable.
- Adjusts the coordination gap between the injection punch and the chamber.
- Rational gate system design
9. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the mechanical strains
Answer: (1) characteristics: the surface which along the mold release direction has scratches.
(2) Causes:
- Incorrect design and manufacturing of molds, such as the forming parts of the core without a slope or negative slope.
- Impressions on the core or cavity walls affect the mold releasing process.
- There is deflection when the casting is ejected.
(3) Preventions:
- Fixes the sites with strains and then checks the mold, modifying the slope, brightening impressions.
- If there are no fixed positions on the strained surface, be aware of adding the coating.
- Inspect the composition of alloys, such as the iron content of the aluminum alloys should not be less than 0.6%.
- Adjusts the ejector rod to balance the ejection force.
10. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the strains due to sticking
Answer (1) characteristics: the die casting alloys stick to the cavity wall, causing the strains. In serious situations, it will be broken.
(2) Causes:
- Liquid alloy pouring temperature is too high
- Die casting mold temperature is too high.
- Insufficient amount of coating or incorrect
- Rough forming mold surface
- Incorrect gate system makes the liquid metal impact the core or wall.
- Incorrect material or heat treatment lead to insufficient stiffness.
- Iron content of aluminum alloy is less than 0.6%.
- Quick filling speed
(3) Preventions:
- Lowers the pouring temperature
- Controls the mold temperature within the processing range
- Eliminates the rough cavity surface
- Inspect the type of the coating or whether the used amount is appropriate.
- Adjusts the inlet to prevent the liquid metal from direct impacting.
- Check the alloy composition to make the iron content in aluminum alloys meets the standard.
- Whether the materials of molds, heat treatment, and stiffness are appropriate.
- Appropriately lowering the filling speed
11. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the collision
Answer: (1) characteristics: scratches and collisions on the casting’s surface
(2) Causes:
- Improper using or transportation
- Improper transmission and loading and unloading
(3) Preventions:
- Be aware of the usage, transportation, and packaging of the products.
- Be careful with removing the parts from the die casting machines.
12. The characteristics, causes, and preventions of the air holes
Answer: (1) characteristics: the inspection of the appearance or the flaw detection after the anatomy: the air holes have a smooth surface. The shape is circular or oval. These air holes often lead to a dark grey surface.
(2) Causes:
- The lead-in direction of the liquid alloy is inappropriate, or the flow velocity of the liquid metal is too fast. This will lead to injection. Plugs the gas exhaust pipes earlier or impacts the wall in front to form vortexes to wrap the air. These air holes are often due to the poor venting effect or deep cavity site.
- The temperature of the liquid metal is too high, containing a large amount of air, so the metal precipitates during solidification.
- A large amount of the gas evolution from the coating gets trapped in the castings.
(3) Preventions:
- Uses clean and dry furnace burden.
- Do not over heat the liquid metal and achieve effective exhaust outcome.
- Alters the flow direction of the gate.
- Lowers the injection speed.
- To ensure the section area of the inlet appropriately.
- The setting of the venting groove should be appropriate and has sufficient venting ability.
13. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the air bubbles
Answer: (1) characteristics: there are many gas concentrated around the casting surface, so there are bubbles on the surface.
(2) Cause:
Caused by the trapped gas:
- The air in the cavity has not voided completely
- The gas formed by coating is easy to be trapped in the castings.
- There are too much air in the liquid metal, which is precipitated on the casting.
- Insufficient cooling time
- The temperature of the partial mold is too high.
(2) Preventions:
- Improves the positions and sizes of the overflow and venting pipes
- Modifies the filling time
- Increases the injection pressure
- Sets core at the positions of the air hole
- Reduces the use of coating
- Eliminates the gas and oxidization in the liquid metal.
- The furnace burden should be well managed to prevent it from being polluted by dust and oil.
- High mold temperature need to be partially cooled.
14. Characteristics, causes, preventions of the shrinkage cavities and porosity.
Answer (1) characteristic: the inspection of appearance or flaw detection after the anatomy: the surface color of the shrinkage cavities is dark, un-smooth, irregular shapes of air holes, large and concentrated are shrinkage cavities. Small and scattered is shrinkage porosity.
(2) Causes: shrinkage cavities are the holes caused by the insufficient internal compensation in the cooling process.
- High pouring temperature
- Low injection-specific pressure
- Big change in wall thickness in the structure of the casting
- Low thickness of inlet
- Short filling time of liquid metal
(3) Preventions:
- Improves the structure of casting for an uniform wall thickness
- Lowers the pouring temperature under the possible conditions
- Increases the injection-specific pressure
- Improves the pouring system to better transferring the pressure
- Adjusts the filling time properly
15. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the cracking
Answer (1) characteristics: put the casting into the alkaline solution. The cracks are dark grey. The damage to the metal base and the Split in a straight line or wavy shape. The grain is narrow and long and has a development trend under the action of external force.
(2) Causes: cracks due to the external force or stress
- The iron content in the aluminum alloy is high, or the silicone content is too high or too low.
- The impurities content is too high in alloys, which reduces the formability of the alloys.
- Temperature of mold core is too low.
- Wall thickness changes are dramatic.
- Injection-specific pressure is low. The strength of the products is insufficient.
- Time for mold retention is long.
- non-informal force during ejection.
- There are impedes and drawing breakage in mold opening, core pulling, or the product ejecting.
(3) Preventions:
- Correctly control the alloy composition. Under some circumstances, it is advisable to add some pure aluminum ingots to lower the iron and silicone content in alloys or add an Al-Si master alloy to increase the silicone content.
- Increases the mold temperature.
- Improves the structure of the castings.
- Adjusts the mold to make the ejector rod under the uniform force.
- Improves the structure to smooth the mold release.
16. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the unclear outline.
Answer: (1) characteristics: the liquid metal has filled the cavity. There are irregular holes and sinks on the surface and uneven edges and corners. The surface shape is natural fluid flow or similar to the liquid level.
(2) Causes:
- The width of inlet is not enough or poor venting conditions.
- Poor fluidity of the alloys.
- Low pouring temperature, mold temperature or the injection speed.
- Insufficient injection-specific pressure.
- Incorrect edges and corners structure and sizes make it hard for filling.
(3) Preventions:
- Modifies the inlet and improves the venting conditions.
- Increases the mold temperature and the pouring temperate of the liquid alloy appropriately.
- Increases the injection -specific pressure or the injection speed.
- Modifies the structures and the sizes of products.
17. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the deformation
Answer: (1) characteristics: bending and distortion in castings that exceed the requirements of the size tolerance of drawing.
(2) Causes:
- Incorrect casting structure and un-uniform contraction on each part.
- The time for mold retention is too short.
- Casting is deviated in the ejection process. The distribution of the eject pins is unreasonable.
- Insufficient rigidity.
- Incorrect positioning or gate-remove methods
- Improves the structure of the castings to get a uniform wall thickness.
- Do not stack castings, especially the large thin walled castings.
- Do not stack into the furnace in the aging or annealing.
- It can be reshaped when necessary.
18. Characteristics, causes, preventions of flashing
Answer: (1) characteristics: the parting surface or the excessive sheet metal protruding from the moving part.
- Inappropriate machine modification before the injection. The mold is not locked.
- The slide the die casting mold is damaged or the locking parts invalid.
- Insert and slide are worn or the fit clearance is inappropriate.
- Insufficient rigidity of the die casting mold leads to deformation.
- The parting surface is not cleaned thoroughly.
- The bulging force is greater than the clamping force.
(3) Preventions:
- Insect the clamping force and the pressurization status.
- Adjusts the pressurized construction to lower the injection-pressurized apex value.
- .inspect the deformation extent or locking parts of die casting mold.
- Inspect whether the die casting mold is damaged.
- Cleans the parting surface.
- Production of machines with large die changing and clamping force.
19. Characteristics, causes, preventions of overfeeding or strip.
Answer:
(1)Characteristics: there are irregular convex parts on the casting (appear repeatedly).
(2) Causes:
- Improper heat treatment to the die casting mold will lead to the collapse.
- crazing leads to the drop piece of the die casting molds.
- The die casting mold with slide is damaged due to the uncleaned parting surface when mold clamping.
- Mechanical damages on the surface.
(3) Preventions:
- Perform heat treatment according to process specification
- Perform according to the process specification rigorously.
- Preventions of crazing
20. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the shift
Answer: (1)characteristics: the parting line is not aligned, steps appeared.
(2)Causes:
- The mold insert shift
- The guide components of the die casting molds shift or worn.
- The die casting mold cavity has errors.
(3)Preventions:
- Adjusts the position of the inserts
- Replaces the guide components.
- Modifies or eliminates the errors.
21. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the unstandardized chemical composition.
(2) Causes:
- Inaccurate ingredients.
- The raw material and the furnace burden have not been analyzed before put into use.
- The time for the melting is too long, so some elements burned too much.
- Impurities mixed in during the melting process.
(3) Preventions:
- The furnace burden should be examined before use.
- The furnace burden should be controlled strictly. New and old furnace burden should be used according to a specific ratio.
- Strictly control the melting processing.
- The melting tools need to spray the coating
22. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the slag inclusion.
Answer : (1) characteristics: irregular visible and invisible holes that are often full of slag. During the appearance inspection, they are black or transparent under the low-power microscope.
(2) Causes: slag or non-metal residual in the mold cavity or metals, which are not cleaned thoroughly before injection.
- The liquid metal surface has uncleaned slag. Pours the slag and the liquid metal together into the chamber.
- The edge falls off and mixes into liquid metal when using graphite crucible.
- When using the coke oven, there are coke or ash mixed into the liquid metal.
- There are too much graphite piled up in the coating.
(3) Preventions:
- Removes the slag on the metal surface.
- Obey the scooping process of liquid metal
- Install the iron rings on the edge of the graphite crucible.
- Be careful when adding coke and discharging ash or to cover the crucible.
- Apply the coating evenly by appropriate amount.
23. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the brittleness
Answer (1) characteristics: the alloy grains are large, so the castings are easy to break or break. The grains on the fracture are large and luminous.
(2) Causes:
- The alloy is too hot and large or the temperature maintaining time is too long.
- The aluminum alloy has too much impurities, like zinc and iron.
- The cooling time of the die casting mold is too long and mold temperature is too high.
- The copper content of the aluminum alloy exceeds the standard range.
(3) Preventions:
- The alloy should not be too hot. Shortens melting or temperature maintaining time as much as possible.
- Improves the cooling conditions of Zinc die casting mold. Shortens the time of cold mold.
- Strictly control the content of alloys within the acceptable range.
24. Characteristics, causes, and preventions of the leakage
Answer: (1)characteristics:pressure test (air tightness) test: Water leakage or seepage.
- There are cracks on castings, mainly caused by the contraction stress.
- Incorrect casting structure, non-uniform wall thickness, leading to the porosity structure.
- The injection force and the injection-specific pressure are insufficient.
- Irrational gate system design.
- Incorrect selection of the alloys.
- Poor venting
(3) Preventions:
- Modifies the product structure and to use the fillet as much as possible to overcome the non-uniform wall thickness.
- Increases the injection-specific pressure.
- Avoid the post treatment as much as possible.
- Improves the gate system and venting system.
- Selects the fine alloys.Quality control
- For products has high requirements need the immersing treatment.

Try GREFEE now,for free
We keep your uploaded files confidential and secure.